For awesome blog #HERE
Adsense s
Labels
Popular Posts
-
"All About You" [Danny:] It's all about you ( [Tom:] It's about you) It's all about you, baby ( [Tom:] It's all ...
-
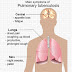
What are the Symptoms of Tuberculosis? A person infected with TB is usually symptom free. Once the infection flares into disease th...
-
Most people are aware of the fact that a diet that’s too rich in sugar and the lack of physical activity can make them prone to gaining e...
-
10 Reasons Why You Should Get More Healthy Oils In Your Diet (with recommendations) ...
-
OURA RING Wearable tech so far is all about the wrist. Fitness bands and smartwatches may be the devices of choice at the mo...
-
Have a question? Send me an e-mail . I try to respond within 24 hours. Please wait at least 48 hours before e-mailing again if I do not r...
-
A new study published in Sleep has reinforced the importance of getting a good night's sleep. Researchers have demonstrated that not ...
-
ABOUT TB Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobact...
-
This is a blog which focuses on lifestyle news, health, and entertainment. Welcome to terhebatdanterbaek – the place to be if you wish to...